As fossil fuel reserves are inching closer to reaching the bottom of the barrel, the need for renewable energy sources is critical now more than ever before. In addition to solar, geothermal, and hydroelectric sources, wind power is another efficient and cost-effective alternative to generating electricity. Evolving from windmills, which have reportedly been used since 500 A.D., wind turbines are the windmill’s mighty predecessors. Towering at heights of up to 853 feet, these “green” giants are efficiently spinning throughout the year and are powering thousands of homes and communities in the process. As we look towards a greener future, wind turbines will be a mighty asset in reducing carbon emissions and air pollution in general.
The Power Generation
According to the Renewables 2019 Global Status Report, between the years 2008 and 2018, wind power alone generated a total of 591 gigawatts (GW) of power. Knowing that the average U.S. household consumes a reported 10,649 kWh annually, 591 GW of energy can power 55,498 homes for a whole year! Additionally, wind power generated another 60.4 GW of power in 2019 alone. As more and more wind farms are put into operation, millions upon millions of tons of CO2 emissions are avoided. According to Clean Power, “wind helps avoid 198 million metric tons of CO2 emissions annually—equivalent to 43 million cars’ worth of emissions.”
Wind turbines are quickly becoming a main contributor to global energy production. As renewable energy sources continue to be used in place of fossil fuels, CO2 emissions will continue to be reduced and we will be able to look forward to a more sustainable future.
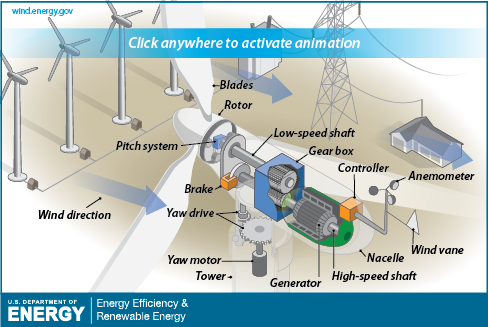
How Wind Turbines Work
So how do wind turbines work, and why are they so efficient? First, wind turbines are built to operate both on land and sea. Many of us have likely driven past wind farms along a freeway or in the countryside, but companies such as Siemens, Vestas, and General Electric are also building wind farms offshore and along coastlines. As these companies strategically place turbines in land areas with plenty of wind, there is also certainly a great deal of wind to be utilized hundreds of feet above our oceans.
There are two types of systems utilized by wind turbines to generate electricity. The first is through the use of a gear box in which the rotor rotation passes through several small gears which connect to a small generator. Since the blades (due to their enormous size and weight) rotate too slowly to generate much electricity on their own, the usage of smaller gears within the gearbox amplifies that rotation over 100 times to more efficiently generate electricity.
The second type of wind turbine is known as a “direct drive turbine”, which does not use a gear box, but rather uses a magnetic generator to convert wind into electricity.

Environmental Concerns & Solutions
Although wind turbines do not release harmful emissions, there is some cause for concern regarding the disposal of materials after a turbine has reached the end of its life. Thankfully, a reported 85%
of the components used in wind turbine production are reusable, according to Evwind News. The blades however, which are made of fiberglass or carbon fiber, are not reusable and are either buried in landfills or burned through pyrolysis.
As these methods are certainly not eco-friendly, one alternative to combat this waste was suggested by Global Fiberglass Solutions, based out of Sweetwater, Texas. On January 8, 2019, they began selling manufacturing-grade pellets called “EcoPoly Pellets”—which are tiny pellets made entirely of ground-up wind turbine blade materials. Instead of lying in landfills, wind turbine blades can be ground into these pellets to then be used in construction and manufacturing, according to EcoPoly Pellets. Another successful alternative was created by Carbon Fiber Recycling, which is a company capable of recycling 100% of the materials used in wind turbine blades. Thankfully, with these solutions invented by
Global Fiberglass Solutions, Carbon Fiber Recycling, and others, the large concerns revolving around a wind turbine’s use after decommission are being resolved in eco-friendly ways.
Powering A Cleaner Future
Wind turbines are increasingly becoming an integral part in the complex task of producing energy throughout the world. As fossil fuels continue to be burned at alarming rates, the need for renewable energy sources is critical to preserve a sustainable future. As it contributed nearly 6% of global energy production in 2019, a large portion of the 27.3% of energy generated globally from renewable sources, wind power is being more abundantly utilized as a cleaner, greener alternative to generating electricity. Wind energy is an emerging asset throughout the world to power a cleaner future.
Keep up with all of Green Living’s original content online and on social media.






